Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose . Identify examples of and differentiate between sugar sources and sugar sinks in plant tissues. Energy is yielded when it is needed. Recent studies have shown that a. sucrose transport is favorable for the following reasons: (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy than 1 mol of a. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. inside the cells, sucrose is converted back to glucose and fructose. food is synthesized in the green parts of a plant. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. Recent studies have shown that a specific transporter protein plays. Explain the roles of solute potential,. in seeds and bulbs, food is stored in polymers (such as starch) that are converted by metabolic processes into sucrose for newly developing plants.
from glossary.periodni.com
Identify examples of and differentiate between sugar sources and sugar sinks in plant tissues. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. Explain the roles of solute potential,. in seeds and bulbs, food is stored in polymers (such as starch) that are converted by metabolic processes into sucrose for newly developing plants. sucrose transport is favorable for the following reasons: food is synthesized in the green parts of a plant. (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy than 1 mol of a. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. inside the cells, sucrose is converted back to glucose and fructose. Recent studies have shown that a specific transporter protein plays.
Sucrose Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary
Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy than 1 mol of a. Recent studies have shown that a. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. food is synthesized in the green parts of a plant. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. Energy is yielded when it is needed. (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy than 1 mol of a. sucrose transport is favorable for the following reasons: inside the cells, sucrose is converted back to glucose and fructose. Explain the roles of solute potential,. Identify examples of and differentiate between sugar sources and sugar sinks in plant tissues. in seeds and bulbs, food is stored in polymers (such as starch) that are converted by metabolic processes into sucrose for newly developing plants. Recent studies have shown that a specific transporter protein plays.
From www.researchgate.net
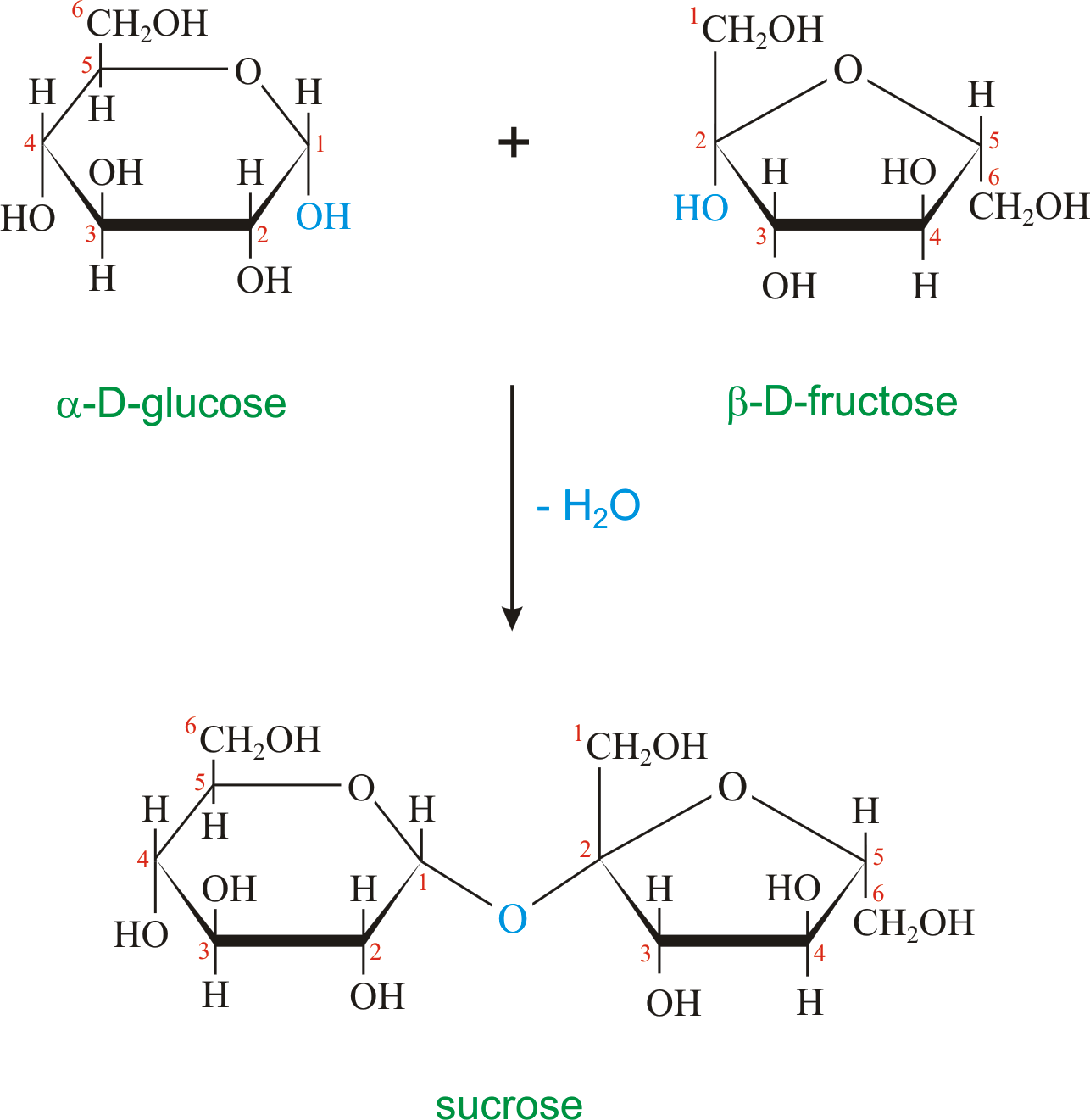
Diagram showing the synthesis of sucrose from glucose and fructose, and Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose in seeds and bulbs, food is stored in polymers (such as starch) that are converted by metabolic processes into sucrose for newly developing plants. (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy than 1 mol of a. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. Energy is yielded when it is needed. sucrose transport is. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From www.researchgate.net
Extracellular hydrolysis of sucrose allows other cells to share glucose Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. food is synthesized in the green parts of a plant. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. Explain the roles of solute potential,. inside the cells, sucrose is converted back to glucose and fructose. Energy is yielded when it is needed.. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From wholeisticliving.com
A Comprehensive List of Foods High in Sucrose Jenna Volpe, RDN, LD Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose Explain the roles of solute potential,. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. inside the cells, sucrose is converted back to glucose and fructose. sucrose transport is favorable for the following reasons: food is synthesized in the green parts of a plant. (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy than 1 mol. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From www.nagwa.com
Question Video Stating the Sugar that Glucose is Stored as in Plants Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy than 1 mol of a. Recent studies have shown that a. inside the cells, sucrose is converted back to glucose and fructose. in seeds and bulbs, food is stored in polymers (such as starch) that are converted by metabolic. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From www.frontiersin.org
Frontiers An Overview of Sucrose Synthases in Plants Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose Explain the roles of solute potential,. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. in seeds and bulbs, food is stored in polymers (such as starch) that are converted by metabolic processes into sucrose for newly developing plants. Recent studies have shown that a. Identify examples of and differentiate between sugar sources and sugar sinks. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From www.researchgate.net
Sucrose (Suc) loading, transport and unloading pathways in a Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose food is synthesized in the green parts of a plant. Explain the roles of solute potential,. Identify examples of and differentiate between sugar sources and sugar sinks in plant tissues. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. sucrose transport is favorable for the following reasons: Recent studies have shown that a specific transporter. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From www.diffordsguide.com
Sucrose, fructose and glucose sugars Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose sucrose transport is favorable for the following reasons: Identify examples of and differentiate between sugar sources and sugar sinks in plant tissues. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. inside the cells, sucrose is converted back to glucose and fructose. (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy than 1 mol of a. . Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From glossary.periodni.com
Sucrose Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy than 1 mol of a. food is synthesized in the green parts of a plant. Identify examples of and differentiate between sugar sources and sugar sinks in plant tissues. Explain the roles of solute potential,. Energy is yielded when it is needed. inside the cells, sucrose is converted back to glucose. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From www.bankofbiology.com
Transport in Plants Notes Class 11 Part 5 Uptake and Transport Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose Explain the roles of solute potential,. in seeds and bulbs, food is stored in polymers (such as starch) that are converted by metabolic processes into sucrose for newly developing plants. Recent studies have shown that a specific transporter protein plays. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From www.researchgate.net
Schematic diagram on controlling of sucrose transport from source leaf Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. Recent studies have shown that a. Identify examples of and differentiate between sugar sources and sugar sinks in plant tissues. food is synthesized in the green parts of a plant. Recent studies have shown that a specific transporter protein plays. (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From www.peregene.com
Transportation Of Carbohydrates Through Phloem Tissue Transport Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose Energy is yielded when it is needed. inside the cells, sucrose is converted back to glucose and fructose. Recent studies have shown that a. Identify examples of and differentiate between sugar sources and sugar sinks in plant tissues. in seeds and bulbs, food is stored in polymers (such as starch) that are converted by metabolic processes into sucrose. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From www.researchgate.net
Sucrose (Suc) synthesis, metabolism and transport in plant cell Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose Energy is yielded when it is needed. Recent studies have shown that a. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. Recent studies have shown that a specific transporter protein plays. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. sucrose transport is favorable for the following reasons: in seeds and. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From en.wikipedia.org
Sucrose Wikipedia Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy than 1 mol of a. Recent studies have shown that a specific transporter protein plays. sucrose transport is favorable for the following reasons: Explain the roles of solute potential,. Energy is yielded when it is needed. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. inside the cells,. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From www.youtube.com
Sucrose biosynthesis in plants//sucrose synthesis in plants YouTube Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose Explain the roles of solute potential,. (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy than 1 mol of a. food is synthesized in the green parts of a plant. Energy is yielded when it is needed. Identify examples of and differentiate between sugar sources and sugar sinks in plant tissues. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From www.researchgate.net
Structural formula of the sucrose (glucose+fructose). Download Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy than 1 mol of a. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. Recent studies have shown that a specific transporter protein plays. inside the cells, sucrose is converted back to glucose and fructose. in. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From www.researchgate.net
Sucrose Unloading, Metabolism, and Transport to AM Fungi. Download Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose Explain the roles of solute potential,. in seeds and bulbs, food is stored in polymers (such as starch) that are converted by metabolic processes into sucrose for newly developing plants. Recent studies have shown that a. (i) 1 mol sucrose contains more energy than 1 mol of a. Identify examples of and differentiate between sugar sources and sugar sinks. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From studyingdiagrams.com
Plant Cell Sucrose Cotransporter Diagram Studying Diagrams Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. in seeds and bulbs, food is stored in polymers (such as starch) that are converted by metabolic processes into sucrose for newly developing plants. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution of carbohydrates in plants. sucrose transport is favorable for the following reasons: (i) 1. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.
From www.teachoo.com
Transporation in Plants Class 10 Biology Notess Teachoo Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose in seeds and bulbs, food is stored in polymers (such as starch) that are converted by metabolic processes into sucrose for newly developing plants. Recent studies have shown that a. food is synthesized in the green parts of a plant. Recent studies have shown that a specific transporter protein plays. sucrose transport is essential for the distribution. Why Food Is Transported In The Form Of Sucrose.